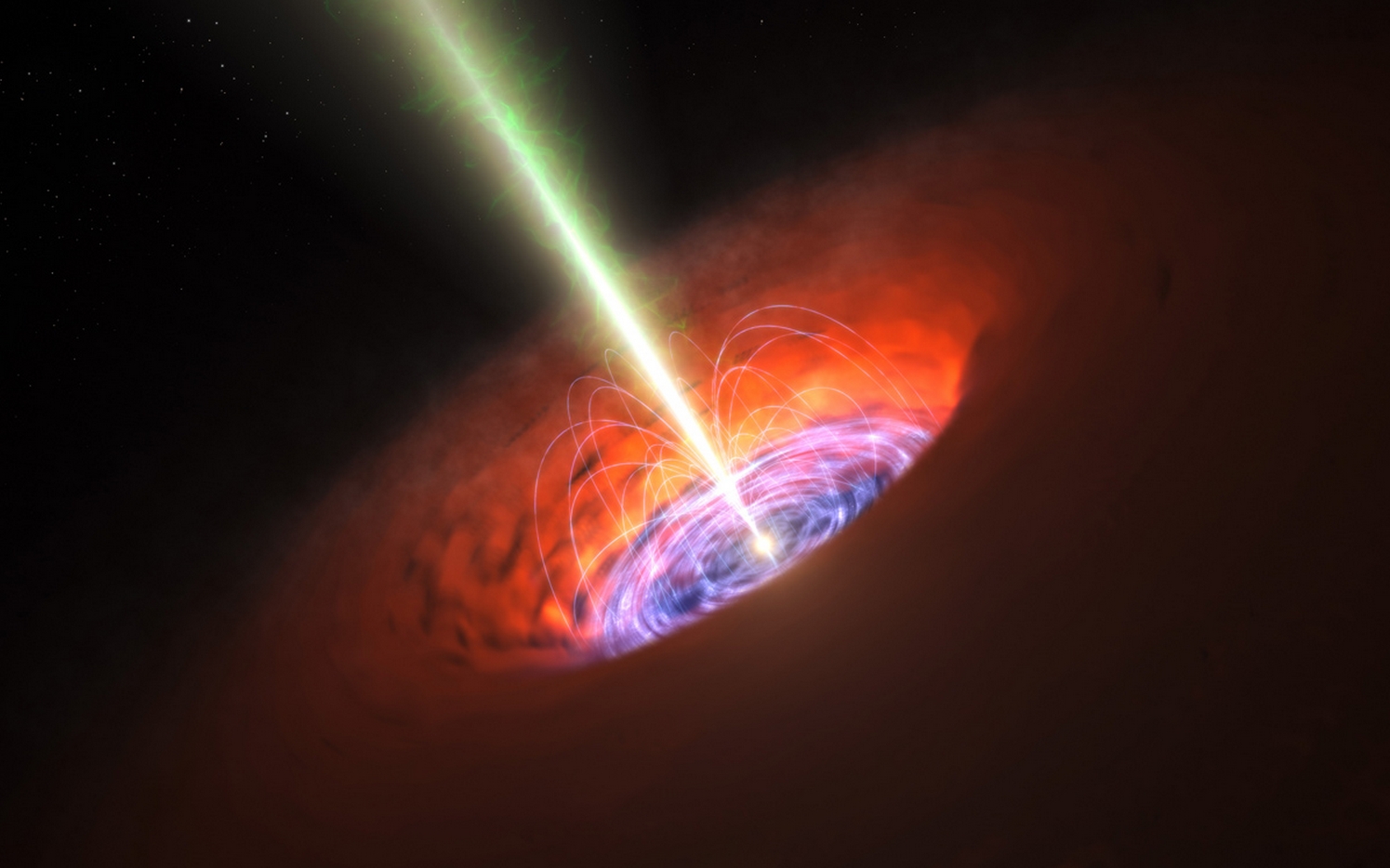
Scientists at Princeton University and the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have developed a rigorous new method for modeling the accretion disk that feeds the supermassive black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
The paper, published online in December in the journal Physical Review Letters, provides a much-needed foundation for simulation of the extraordinary processes involved.
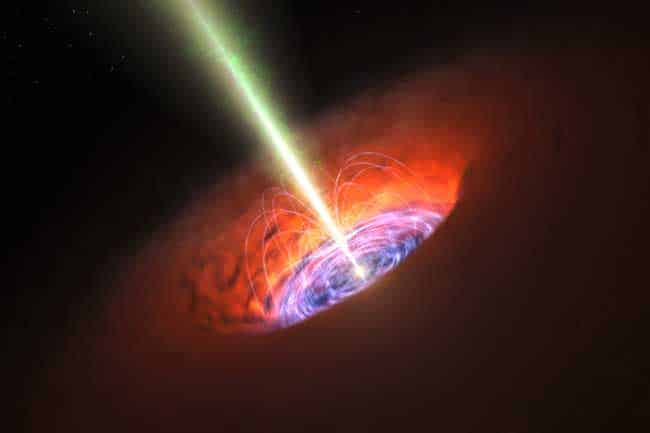
Accretion disks are clouds of plasma that orbit and gradually swirl into massive bodies such as black holes — intense gravitational fields produced by stars that collapse to a tiny fraction of their original size. These collapsed stars are bounded by an “event horizon,” from which not even light can escape. As accretion disks flow toward event horizons, they power some of the brightest and most energetic sources of electromagnetic radiation in the universe.
Four million times the mass of the sun
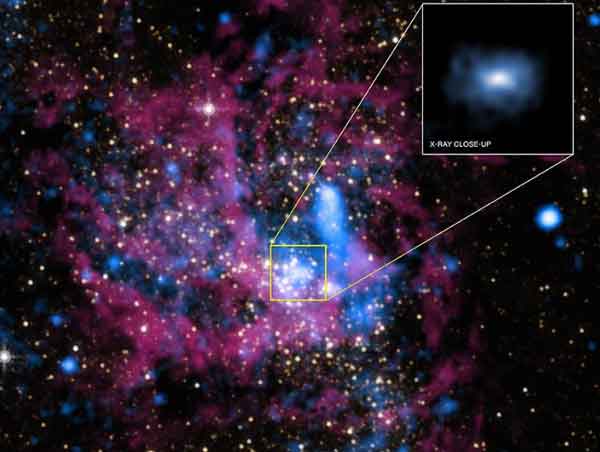
The colossal black hole at the center of the Milky Way — called “Sagittarius A*” because it is found in the constellation Sagittarius — has a gravitational mass that is four million times greater than our own sun. Yet the accretion disk plasma that spirals into this mass is “radiatively inefficient,” meaning that it emits much less radiation than one would expect.[xyz-ihs snippet=”adsense-body-ad”]”So the question is, why is this disk so quiescent?” asks Matthew Kunz, lead author of the paper, assistant professor of astrophysical sciences at Princeton University and a physicist at PPPL. Co-authors include James Stone, Princeton professor of astrophysical sciences, and Eliot Quataert, director of theoretical astrophysics at the University of California, Berkeley.
To develop a method for finding the answer, the researchers considered the nature of the superhot Sagittarius A* accretion disk. Its plasma is so hot and dilute that it is collisionless, meaning that the trajectories of protons and electrons inside the plasma rarely intersect.
This lack of collisionality distinguishes the Sagittarius A* accretion disk from brighter and more radiative disks that orbit other black holes. The brighter disks are collisional and can be modeled by formulas dating from the 1990s, which treat the plasma as an electrically conducting fluid. But “such models are inappropriate for accretion onto our supermassive black hole,” Kunz said, since they cannot describe the process that causes the collisionless Sagittarius A* disk to grow unstable and spiral down.
Tracing collisionless particles
To model the process for the Sagittarius A* disk, the paper replaces the formulas that treat the motion of collisional plasmas as a macroscopic fluid. Instead, the authors use a method that physicists call “kinetic” to systematically trace the paths of individual collisionless particles. This complex approach, conducted using the Pegasus computer code developed at Princeton by Kunz, Stone and Xuening Bai, now a lecturer at Harvard University, produced a set of equations better able to model behavior of the disk that orbits the supermassive black hole.
This kinetic approach could help astrophysicists understand what causes the accretion disk region around the Sagittarius A* hole to radiate so little light. Results could also improve understanding of other key issues, such as how magnetized plasmas behave in extreme environments and how magnetic fields can be amplified.
The goal of the new method, said Kunz, “will be to produce more predictive models of the emission from black-hole accretion at the galactic center for comparison with astrophysical observations.” Such observations come from instruments such as the Chandra X-ray observatory, an Earth-orbiting satellite that NASA launched in 1999, and the upcoming Event Horizon Telescope, an array of nine Earth-based radio telescopes located in countries around the world.
Source: Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory [xyz-ihs snippet=”Adsense-responsive”]