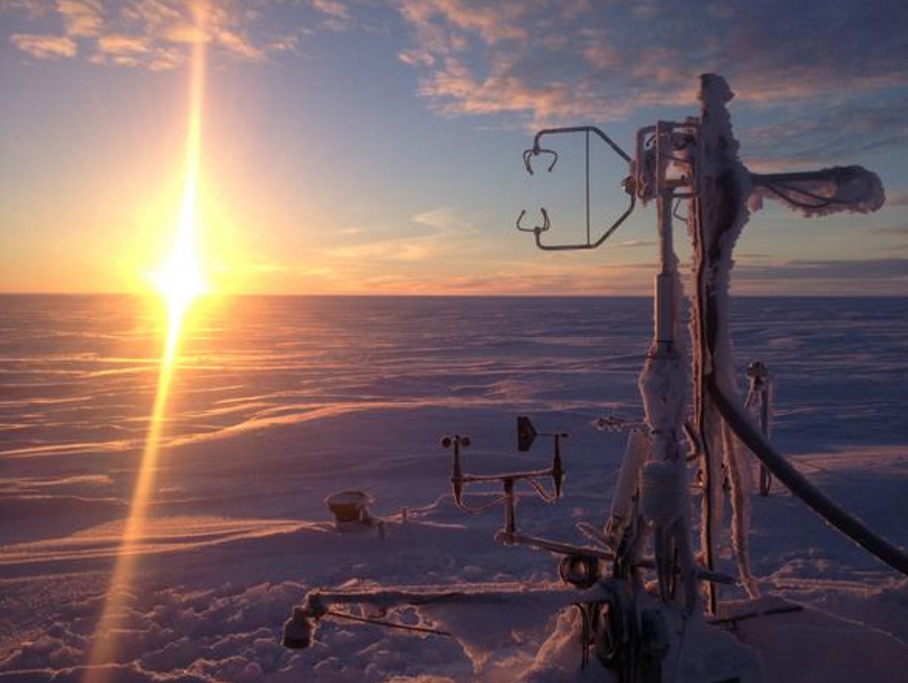
Scientists studying the atmosphere above Barrow, Alaska, have discovered unprecedented levels of molecular chlorine in the air, a new study reports.
Molecular chlorine, from sea salt released by melting sea ice, reacts with sunlight to produce chlorine atoms. These chlorine atoms are highly reactive and can oxidize many constituents of the atmosphere including methane and elemental mercury, as well activate bromine chemistry, which is an even stronger oxidant of elemental mercury. Oxidized mercury is more reactive and can be deposited to the Arctic ecosystem.
The study is the first time that molecular chlorine has been measured in the Arctic, and the first time that scientists have documented such high levels of molecular chlorine in the atmosphere.
“No one expected there to be this level of chlorine in Barrow or in polar regions,” said Greg Huey, a professor in the School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta.
The study was published January 12 in the journal Nature Geoscience and was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), part of the international multidisciplinary OASIS program.
The researchers directly measured molecular chlorine levels in the Arctic in the spring of 2009 over a six-week period using chemical ionization mass spectrometry. At first the scientists were skeptical of their data, so they spent several years running other experiments to ensure their findings were accurate.
The level of molecular chlorine above Barrow was measured as high as 400 parts per trillion, which is a high concentration considering that chlorine atoms are short –lived in the atmosphere because they are strong oxidants and are highly reactive with other atmospheric chemicals.
Molecular chlorine concentrations peaked in the early morning and late afternoon, and fell to near-zero levels at night. Average daytime molecular chlorine levels were correlated with ozone concentrations, suggesting that sunlight and ozone may be required for molecular chlorine formation.
Previous Arctic studies have documented high levels of oxidized mercury in Barrow and other polar regions. The major source of elemental mercury in the Arctic regions is coal-burning plants around the world. In the spring in Barrow, ozone and elemental mercury are often depleted from the atmosphere when halogens — chlorine and bromine — are released into the air from melting sea ice.
“Molecular chlorine is so reactive that it’s going to have a very strong influence on atmospheric chemistry,” Huey said.
Chlorine atoms are the dominant oxidant in Barrow, the study found. The area is part of a region with otherwise low levels of oxidants in the atmosphere, due to the lack of water vapor and ozone, which are the major precursors to making oxidants in many urban areas.
In Barrow, snow-covered ice pack extends in every direction except inland. The ultimate source of the molecular chlorine is the sodium chloride in sea salt, Huey said, most likely from the snow-covered ice pack. How the sea salt is transformed into molecular chlorine is unknown.
“We don’t really know the mechanism. It’s a mystery to us right now,” Huey said. “But the sea ice is changing dramatically, so we’re in a time where we have absolutely no predictive power over what’s going to happen to this chemistry. We’re really in the dark about the chlorine.”
Scientists do know that sea ice is rapidly changing, Huey said. The sea ice that lasts from one winter to the next winter is decreasing. This has created a larger area of melted ice, and more ice that comes and goes with the seasons. This seasonal variation in ice could release more molecular chlorine into the atmosphere.
“There is definite climate change happening in the Arctic,” Huey said. “That’s changing the nature of the ice, changing the volume of the ice, changing the surface area and changing the chemistry of the ice.”
This research is supported by the National Science Foundation under award number ATM-0807702, ARC-0806437 and ARC-0732556. Any conclusions or opinions are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NSF.