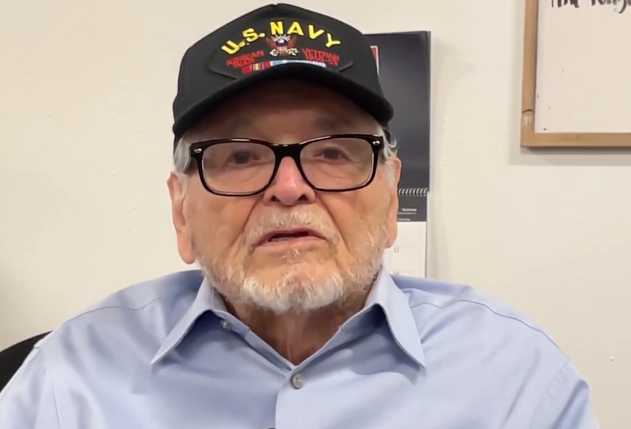
“We’re not the subjugated and disenfranchised people that we were,” said one Ponca elder who took part in the 1973 revolt. “Wounded Knee was an important beginning of that.”

As many Native Americans on Monday marked the 50th anniversary of the militant occupation of Wounded Knee, South Dakota, participants in the 1973 uprising and other activists linked the deadly revolt to modern-day Indigenous resistance, from Standing Rock to the #LandBack movement.
On February 27, 1973 around 300 Oglala Lakota and members of the American Indian Movement (AIM), seething from centuries of injustices ranging from genocide to leniency for whites who committed crimes against Indians, occupied the hamlet of Wounded Knee on the Pine Ridge Reservation for more than two months. The uprising occurred during a period of increased Native American militancy and the rise of AIM, which first drew international attention in 1969 with the 19-month occupation of Alcatraz Island in San Francisco Bay.
“The Native people of this land after Wounded Knee, they had like a surge of new pride in being Native people,” Dwain Camp, an 85-year-old Ponca elder who took part in the 1973 revolt, told The Associated Press.
“Anything that goes on, anything we do, even today with the #LandBack issue, all of that is just a continuation.”
Camp said the occupation drove previously “unimaginable” changes, including the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act, the Indian Child Welfare Act, the American Indian Religious Freedom Act, and the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act.
“After we left Wounded Knee, it became paramount that protecting Mother Earth was our foremost issue,” he explained. “Since that period of time, we’ve learned that we’ve got to teach our kids our true history.”
Camp said the spirit of Wounded Knee lives on in Indigenous resistance today.
The AIM occupation of 1973 endures in a new generation of Native activists at Standing Rock and other protests https://t.co/O0KZn7KF9J
— ICT (@IndianCountry) February 26, 2023
"We're not the subjugated and disenfranchised people that we were," he said. "Wounded Knee was an important beginning of that. And because we're a resilient people, it's something we take a lot of pride in."
Some of the participants in the 1973 uprising had been raised by grandparents who remembered or even survived the 1890 massacre of more than 200 Lakota Lakota men, women, and children by U.S. troops at Wounded Knee.
"That's how close we are to our history," Madonna Thunder Hawk, an 83-year-old elder in the Oohenumpa band of the Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe who was a frontline participant in the 1973 occupation, told Indian Country Today. "So anything that goes on, anything we do, even today with the #LandBack issue, all of that is just a continuation. It's nothing new."
Continue reading at Common Dreams
Common Dream’s work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 License. Feel free to republish and share widely.
[content id="79272"]